About La Sapienza University of Rome
La Sapienza University of Rome
Articles by La Sapienza University of Rome
Hyperacute fatal course in a hypercalcemic crisis
Published on: 20th January, 2021
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 8899339891
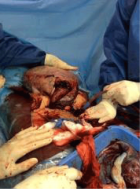
A 39-year-old woman, with a not significant past medical history, entered the Emergency Department complaining about nausea, vomiting, constipation, anorexia, deep asthenia, and diffuse muscle aches with cramps. She referred sporadic diarrhea (one episode) the day before and a worsening headache in the past three days; she also complained about polyuria and polydipsia not investigated for one year. The clinical examination was not significant, apart from the evidence of skin and mucosal dryness, tachycardia, and diffuse abdominal pain. The laboratory tests revealed hypokalemia and elevated beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) plasma levels. An ultrasound abdominal imaging was consistent with kidney lithiasis. Suspecting a hyperemesis gravidarum in a patient with kidney lithiasis, a rehydrating therapy was administered as long as potassium reintegration. During the hospital stay, the patient became drowsy. A haemogasanalysis revealed very high calcium values: 3,379 mmol/L (n.v. 1,120-1,320 mmol/L). Lab tests confirmed very high levels of calcium 21,1 mg/dL (n.v. 9-10,5 mg/dL), as long as increased parathormone (PTH) > 3000 pg/mL (normal values 14-65 pg/mL), and hypokalemia (3,2 mEq/L n.v. 3,50 – 4,50). Ultrasound exam of the neck revealed the presence of a left parathyroid nodule measuring 2,5 x 1,6 cm. Before having time to start an appropriate therapy, the patient died.
Markov Chains of Molecular Processes of Biochemical Materials
Published on: 18th January, 2024
Biochemical systems are analytically investigated after encoding the properties of the dynamics, which rule the time evolution of the transition properties, using some Markov models, such as the Hierarchical Markov-State Models. The present paper is aimed at analytically writing the (finite) Markov chain originating from the considered Markov models. Within this framework, the interaction with the environment is considered, and the ergodicity of the systems obtained from numerical simulation is controlled and compared with the qualities of the Markov chain. The (von Neumann) conditions to be imposed on the Bloch equations for the biomaterial structures to be described analytically in a consistent way are governed. The formalisms of the ’heat bath’ and that of the control of the numerical errors ensure the good measure-theoretical framework and the ergodicity of the finite chain, respectively.The finite Markov chains are investigated and the analytical expressions are presented, after which the Hierarchical Markov-State-Model provides the time evolution of the transition probabilities in biochemical systems.The notion of heat bath is used to describe the interactions of the biomaterial with the environment and thus to control the uses of the projection operators in the Markovian processes where the appropriate measure is defined; the stochastic equations allow one to obtain the wanted measure from the probability spaces.The cases in which a violation of the Markov property of the process occurs, i.e. in open systems, or dissipative processes are also considered. Furthermore, in complex molecules in biological systems, these features are investigated to be possibly even more dramatic. As far as molecular processes are concerned, this occurrence is associated with the appearance of chaotic effects with certain characteristics of potential surfaces: rather than the technique of isocommittors, the method of projectors in measure spaces is used for the Nakajima-Zwanzig paradigm for the density operator; this latter method complementary compares the time-convolution-less technique.The finite Markov chains are finally proven to be ergodic after the control of the numerical errors which provide the Sinai-Markov partitions to be applied for the analysis of the measure space of the Markov chain, that is, one endowed with a Hilbert measure. The von Neumann conditions are therefore newly demonstrated to be apt to be applied to the Bloch equations for biomaterial structures after the use of the notion of heat bath, from which the measure space arises.The qualities of the Hierarchical Markov-Sate Models which bring the analytical expression of the time evolution of probabilities of biomaterials are therefore newly analytically studied.

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."